Tense is an essential component of any language, including Hindi. It helps us understand when an action takes place – in the past, present, or future. In Hindi, tenses are used to express time, duration, and frequency, making them vital for constructing accurate sentences. In this article, we will explore the different types of tense in Hindi, their structures, and how to use them effectively in various contexts.
Types of Tense in Hindi
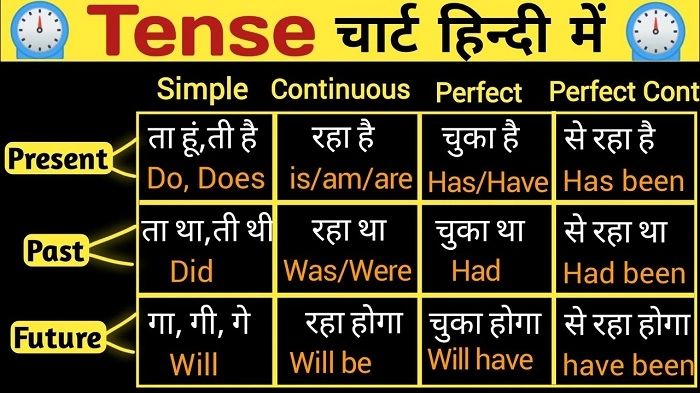
In Hindi, tenses are broadly classified into three main categories: Present Tense, Past Tense, and Future Tense. These are further divided into simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous forms. Let’s dive into each one.
1. Present Tense (वर्तमान काल)
Present tense is used to describe actions happening currently, general truths, habits, or repeated actions. It is further categorized into three subtypes.
Simple Present Tense (साधारण वर्तमान काल)
This tense is used to express habitual actions, general truths, and facts.
Structure: Subject + Verb (in the base form) + Object
Example:
- मैं पढ़ता हूँ। (Main padhta hoon.) – I read.
Present Continuous Tense (वर्तमान काल निरंतर)
The present continuous tense describes actions that are happening at the moment of speaking or are ongoing.
Structure: Subject + is/are/am + Verb (in the continuous form) + Object
Example:
- मैं पढ़ रहा हूँ। (Main padh raha hoon.) – I am reading.
Present Perfect Tense (वर्तमान पूर्ण काल)
This tense expresses actions that were completed in the recent past and have relevance in the present.
Structure: Subject + has/have + Verb (in the past participle) + Object
Example:
- मैंने किताब पढ़ ली है। (Maine kitaab padh li hai.) – I have read the book.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense (वर्तमान पूर्ण निरंतर काल)
This tense indicates an action that began in the past and is still continuing, with a focus on the duration of the action.
Structure: Subject + has/have + been + Verb (in the continuous form) + Object
Example:
- मैं पढ़ रहा हूँ। (Main padh raha hoon.) – I have been reading.
2. Past Tense (भूतकाल)
The past tense describes actions that have already happened. Like the present tense, it also has different subtypes.
Simple Past Tense (साधारण भूतकाल)
This tense is used to describe actions that have been completed in the past.
Structure: Subject + Verb (in the past form) + Object
Example:
- मैंने खाना खाया। (Maine khana khaya.) – I ate food.
Past Continuous Tense (भूतकाल निरंतर)
Used for actions that were happening at a particular time in the past.
Structure: Subject + was/were + Verb (in the continuous form) + Object
Example:
- मैं पढ़ रहा था। (Main padh raha tha.) – I was reading.
Past Perfect Tense (भूतकाल पूर्ण काल)
This tense indicates an action that was completed before another action in the past.
Structure: Subject + had + Verb (in the past participle) + Object
Example:
- मैंने खाना खा लिया था। (Maine khana khaa liya tha.) – I had eaten the food.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense (भूतकाल पूर्ण निरंतर काल)
This tense describes an action that had been happening for some time before another action took place.
Structure: Subject + had + been + Verb (in the continuous form) + Object
Example:
- मैं दो घंटे से पढ़ रहा था। (Main do ghante se padh raha tha.) – I had been reading for two hours.
3. Future Tense (भविष्यकाल)
Future tense is used to describe actions that will happen after the present time. Like the other tenses, it has subtypes.
Simple Future Tense (साधारण भविष्यकाल)
This tense expresses an action that will happen in the future.
Structure: Subject + will/shall + Verb (in the base form) + Object
Example:
- मैं खाना खाऊँगा। (Main khana khaoonga.) – I will eat food.
Future Continuous Tense (भविष्यकाल निरंतर)
Used to describe an action that will be happening at a specific point in the future.
Structure: Subject + will/shall + be + Verb (in the continuous form) + Object
Example:
- मैं पढ़ रहा होऊँगा। (Main padh raha hoonga.) – I will be reading.
Future Perfect Tense (भविष्य पूर्ण काल)
This tense describes an action that will be completed before a specific time or event in the future.
Structure: Subject + will/shall + have + Verb (in the past participle) + Object
Example:
- मैंने किताब पढ़ ली होगी। (Maine kitaab padh li hogi.) – I will have read the book.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense (भविष्य पूर्ण निरंतर काल)
This tense indicates an action that will be ongoing until a specific time in the future.
Structure: Subject + will/shall + have + been + Verb (in the continuous form) + Object
Example:
- मैं दो घंटे से पढ़ रहा होऊँगा। (Main do ghante se padh raha hoonga.) – I will have been reading for two hours.
Key Points to Remember
- Tenses express time: Present, past, and future tenses reflect when the action occurs.
- Verb forms change: The verb form changes according to the tense, reflecting whether the action is simple, continuous, perfect, or perfect continuous.
- Use of auxiliary verbs: Words like “is,” “are,” “am,” “was,” “were,” “will,” and “have” are used to form various tenses in Hindi.
FAQs
What is the difference between present perfect and present continuous tense in Hindi?
Present perfect tense talks about actions that were completed recently and have relevance to the present, while present continuous tense is used for actions happening at the moment.
How can I use the future perfect tense in Hindi?
To express an action that will be completed before a certain point in the future, use the structure: Subject + will/shall + have + Verb (past participle).
Can you explain the use of the past perfect continuous tense in Hindi?
The past perfect continuous tense is used to describe an ongoing action that was happening before another event in the past. Example: “मैं पढ़ रहा था” (Main padh raha tha) – I had been reading.
What are the rules for forming future tense in Hindi?
For future tense, use “will/shall” followed by the base form of the verb. For continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous forms, auxiliary verbs like “will be” or “will have” are used.
How do I use the present tense in Hindi?
The present tense is used for actions happening now, habitual actions, or general truths. Use “हूँ” (hoon), “है” (hai), or “हैं” (hain) depending on the subject.